PCR 광학계 구성


PCR[ Polymerase Chain Reaction]검사(코로나19 검사) 방법
의심 환자의 침이나 가래 등 가검물에서 RNA를 채취해 진짜 환자의 RNA와 비교해 일정비율 이상 일치하면 양성으로 판정하는 검사방법. 출처 : 매일경제용어사전
검사방법
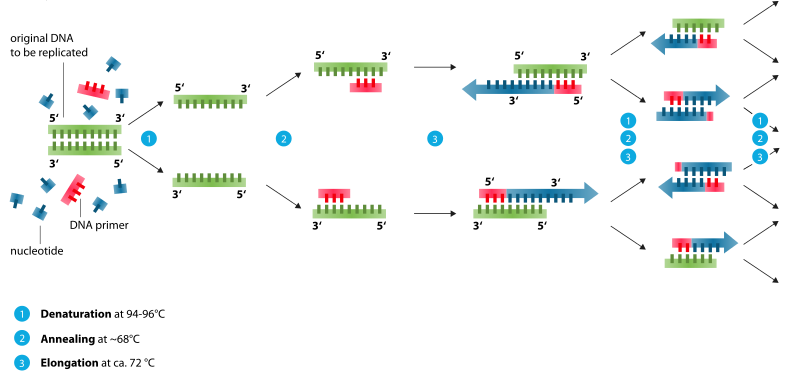
중합효소 연쇄 반응의 순서는 3단계로 이루어진다.
1. 열을 이용하여 두 가닥의 DNA를 분리하는 열변성 과정(denaturation)을 거친 후,
2. 온도를 낮추어 시발체(primer)가 증폭을 원하는 서열 말단에 결합(annealing)하게 하고,
3. 다시 열을 약간 올려서 DNA를 합성하는 중합 반응(polymerization or extension)을 일으킨다.
열변성 과정은 보통 95℃에서 열을 이용하여 2가닥의 DNA의 상보적인 염기의 수소결합을 1가닥으로 떨어뜨리는 과정이며, 결합 반응은 약 55~65℃에서 한 가닥의 DNA에 시발체가 상보적인 염기서열에 결합하는 과정이다.
마지막으로 중합 반응은 한 가닥의 DNA(주형 DNA)에 시발체가 붙은 다음의 염기에 DNA 중합효소(polymerase)를 이용하여 주형 DNA의 상보적인 염기를 합성하여 두 가닥의 DNA으로 연장시킨다. 그 후 다시 열변성 과정, 결합 반응, 중합 반응을 반복하여 DNA를 증폭하게 된다.
중합효소 연쇄 반응 1회를 시행하면 유전 물질은 2배로 증폭된다. 따라서 반응의 반복에 의한 기하급수적인 증폭이 가능하고, 중합효소 연쇄 반응을 n회를 반복하면 이론상으로 2의 n승배의 유전자가 증폭된다.

중합효소 연쇄 반응의 변형 방법으로는, RNA를 대상으로 역전사효소를 이용하여 역전사 반응을 시행하여 complementary DNA를 합성하여 이를 주형으로 이용하여 중합효소 연쇄 반응을 시행하는 역전사중합효소 연쇄 반응(reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction, RT-PCR)과 형광물질을 사용하여 DNA를 증폭시키면서 증폭산물을 동시에 검출하는 실시간 중합효소 연쇄 반응 등이 있다.
[네이버 지식백과] 중합효소 연쇄 반응 [polymerase chain reaction] (서울대학교병원 의학정보, 서울대학교병원)
fluorescence immunoassay/형광면역분석(법)
일종의 형광반응으로 Sample 형광 물질이 특정 파장의 빛을 흡수하면 형광 물질의 분자가 여기(excitation)되었다가, 다시 원래의 상태로 돌아오면서 흡수한 빛과는 다른 파장(emissino)의 빛을 내는 반응.
Gene-Channels

PCR 형광 테스트

Polymerase chain reaction
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Principles
PCR amplifies a specific region of a DNA strand (the DNA target). Most PCR methods amplify DNA fragments of between 0.1 and 10kilo base pairs(kbp) in length, although some techniques allow for amplification of fragments up to 40 kbp.[5]The amount of amplified product is determined by the available substrates in the reaction, which becomes limiting as the reaction progresses.[6]
Procedure
Typically, PCR consists of a series of 20–40 repeated temperature changes, called thermal cycles, with each cycle commonly consisting of two or three discrete temperature steps (see figure below). The cycling is often preceded by a single temperature step at a very high temperature (>90 °C (194 °F)), and followed by one hold at the end for final product extension or brief storage. The temperatures used and the length of time they are applied in each cycle depend on a variety of parameters, including the enzyme used for DNA synthesis, the concentration of bivalent ions and dNTPs in the reaction, and themelting temperature(Tm) of the primers.[11]
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Polymerase_chain_reaction
'형광면역분석_PCR' 카테고리의 다른 글
| DNA & RNA (0) | 2022.06.22 |
|---|---|
| Fluorescence Fundamentals & PCR Gene Channels (0) | 2022.06.22 |
| PCR(Polymerase chain reaction) 중합효소 연쇄반응 (0) | 2022.05.24 |
| 형광면역분석(PCR)을 위한 핵산 추출 방법 (0) | 2020.12.18 |
| 형광면역분석(법)/fluorescence immunoassay (1) | 2020.11.16 |



